Corvette C7 Chassis
The C7 chassis represents offered many improvements over the C5 and C6 chassis. For the C6, there was a steel chassis for the coupe (which included an open Targa roof) and the convertible. The Z06 and ZR1 models, which were strictly fixed roof designs, were able to take advantage of the performance benefits of an aluminium chassis.
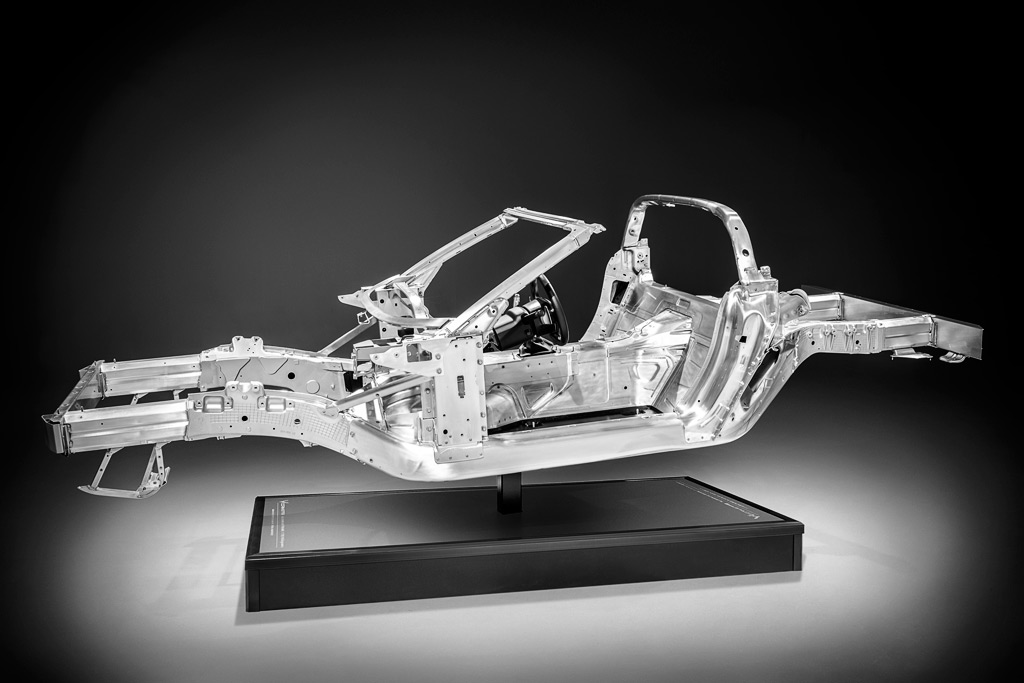
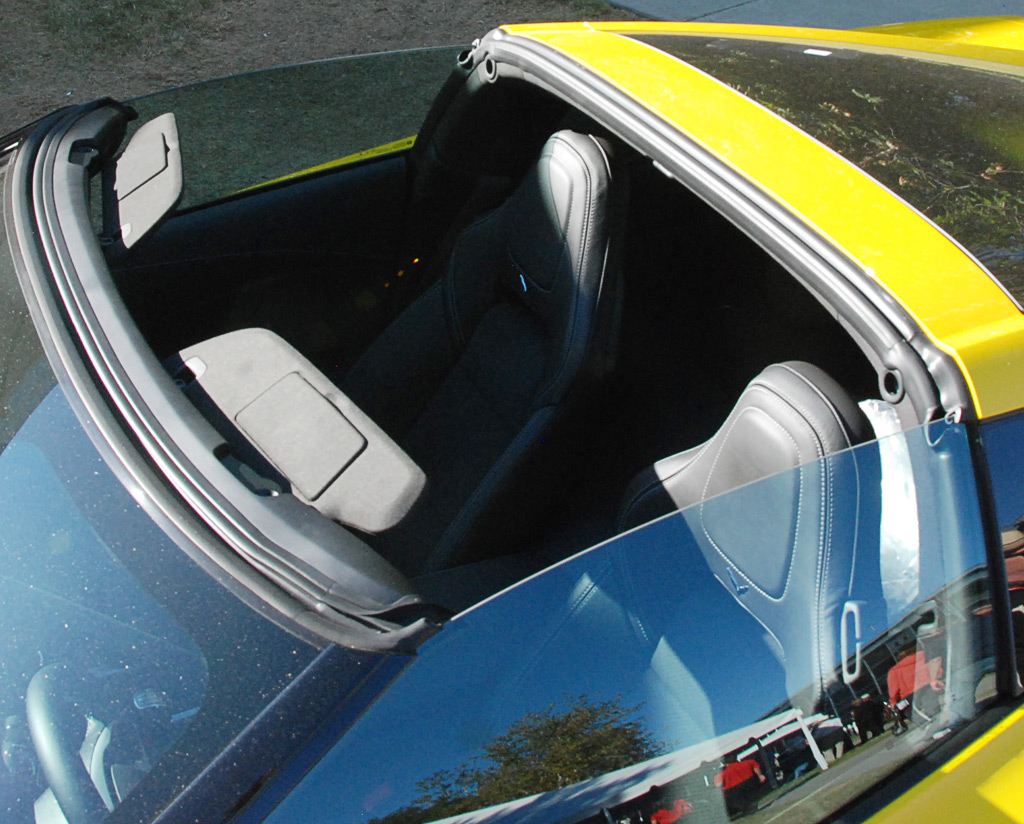
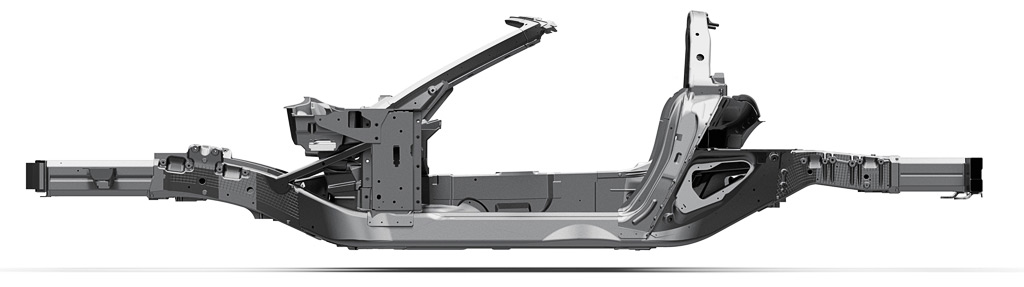
 For 2014 the C7 is an open car since the coupe is equipped with a Targa roof (right). The chassis is all aluminum and offers significant improvements which included lower weight (99 lbs less is claimed) and 57% more torsional rigidity. It is composed of 10 castings, 38 extrusions, 76 stampings and three hydroformed parts. The total weight is 170 kg (374 lbs.).
For 2014 the C7 is an open car since the coupe is equipped with a Targa roof (right). The chassis is all aluminum and offers significant improvements which included lower weight (99 lbs less is claimed) and 57% more torsional rigidity. It is composed of 10 castings, 38 extrusions, 76 stampings and three hydroformed parts. The total weight is 170 kg (374 lbs.).
The wheelbase is approximately one inch longer and the front and rear tracks about an inch wider when compared to the C6. The C7 frame rails are composed of five aluminum segments.
Also on the C7 chassis resume:
- 354 spot-welds using a GM-patented process that uses a unique electrode designed specifically for aluminum
- 188 Flowdrill-machined fasteners, which are installed by a high-speed drill that extrudes the frame material to create a strong, integral collar that is tapped for bolt-on fasteners
- 113 feet of structural adhesives, used in conjunction with welding and fasteners to increase overall frame stiffness
- 37 feet of laser welds, which join frame sections via a precise beam of high energy that minimizes heat beyond the weld area for improved structural accuracy.
2014 Corvette chassis front (above) and rear (below) aluminum extrusions.
Chassis front suspension mount casting.
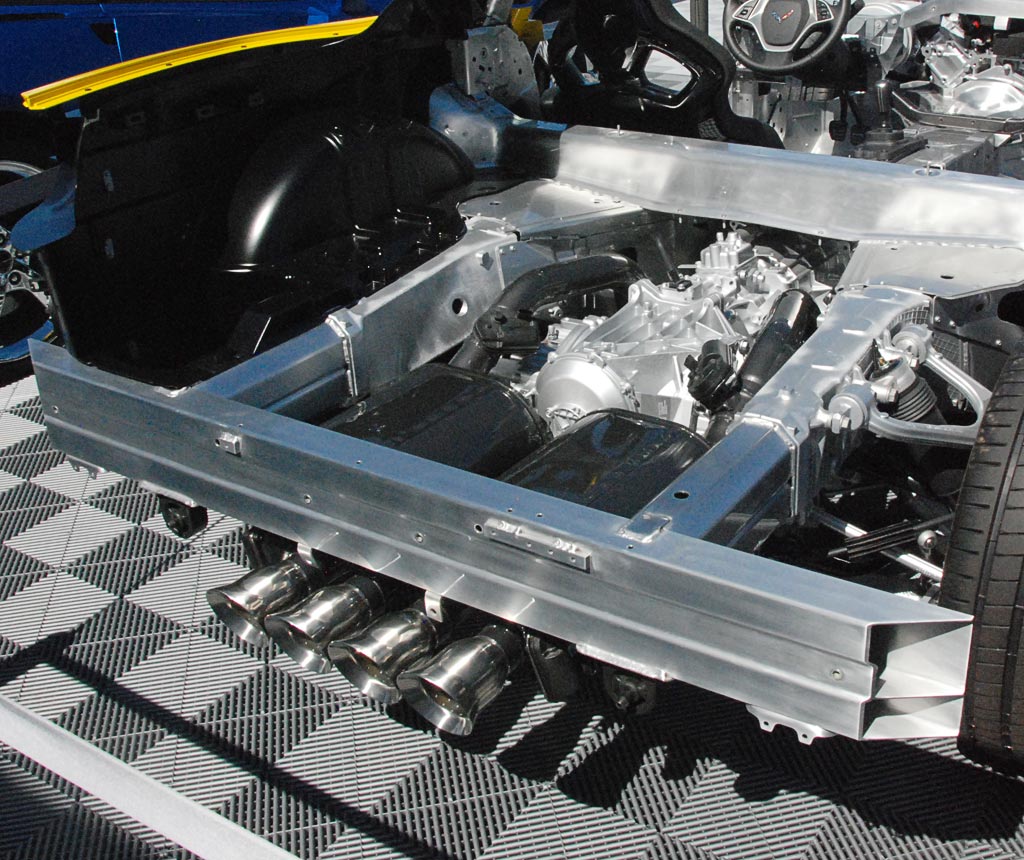
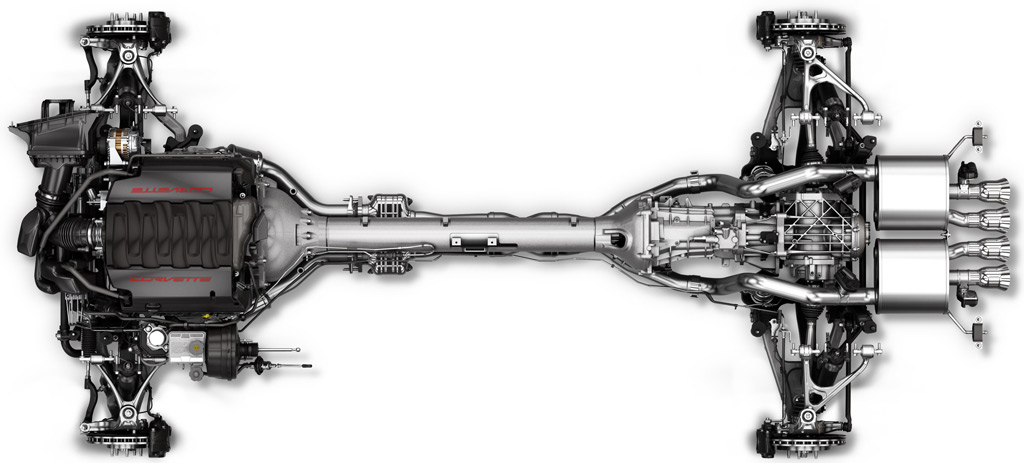
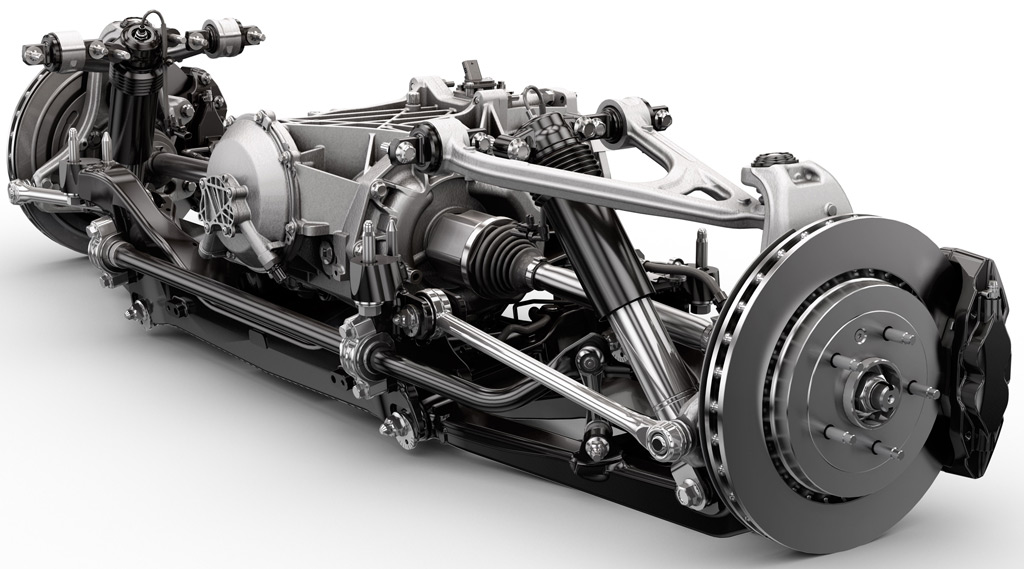
Overhead view of the C7 chassis shows that the torque tube (first seen on the C4 Corvette), which mechanically couples the transaxle, continues.
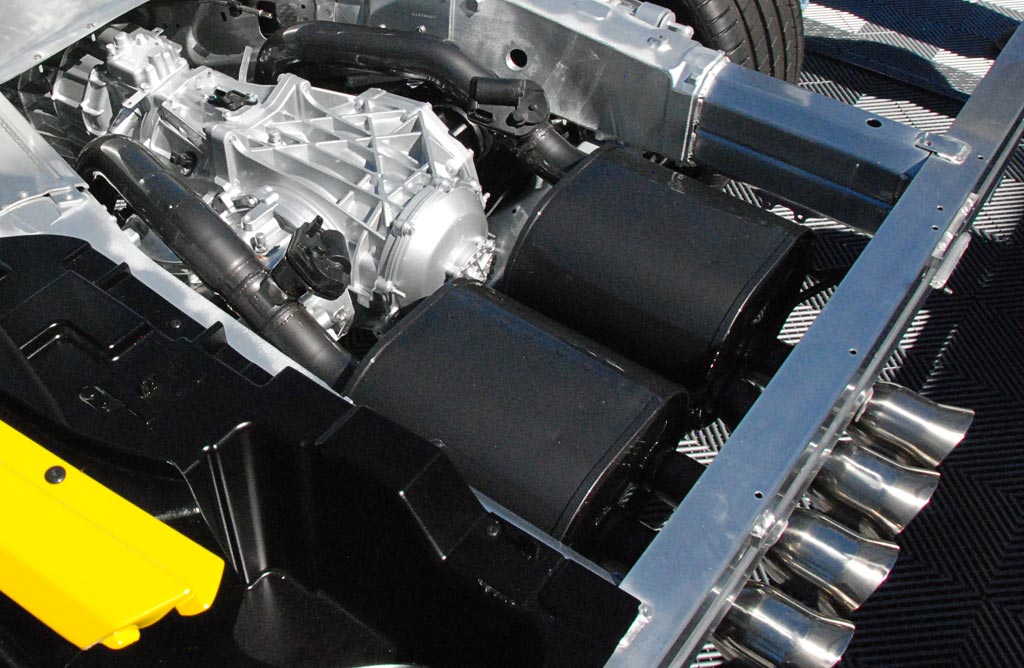
 Also, and perhaps more importantly, the transaxle (right), is located at and in front of the rear axle. First seen on the C5 in 1997, the layout results in a near perfect 50 - 50 weight distribution.
Also, and perhaps more importantly, the transaxle (right), is located at and in front of the rear axle. First seen on the C5 in 1997, the layout results in a near perfect 50 - 50 weight distribution.
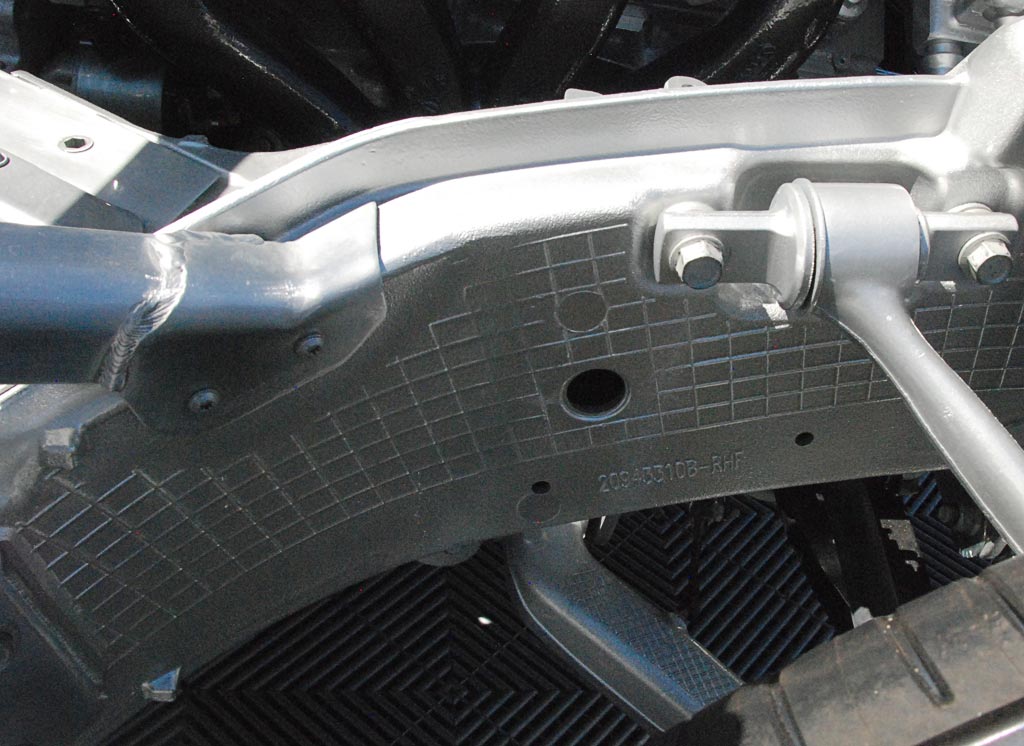
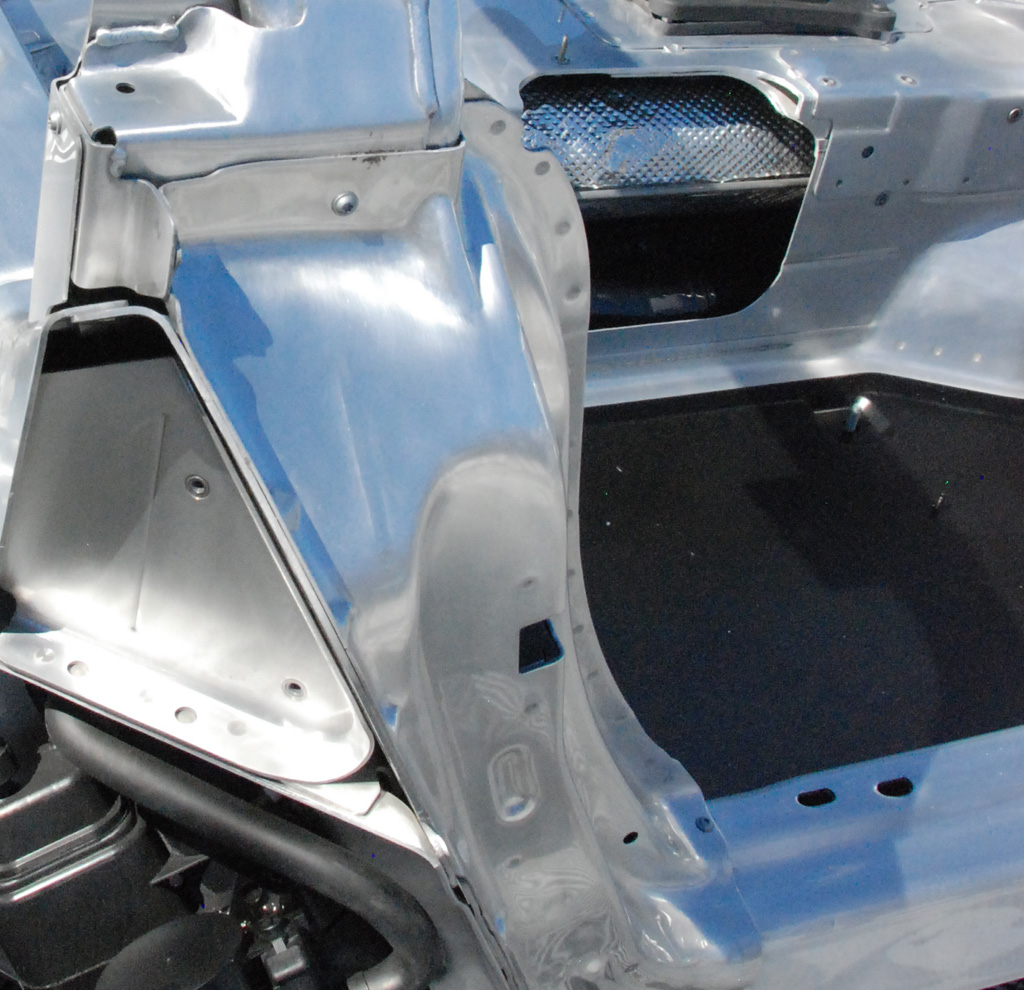
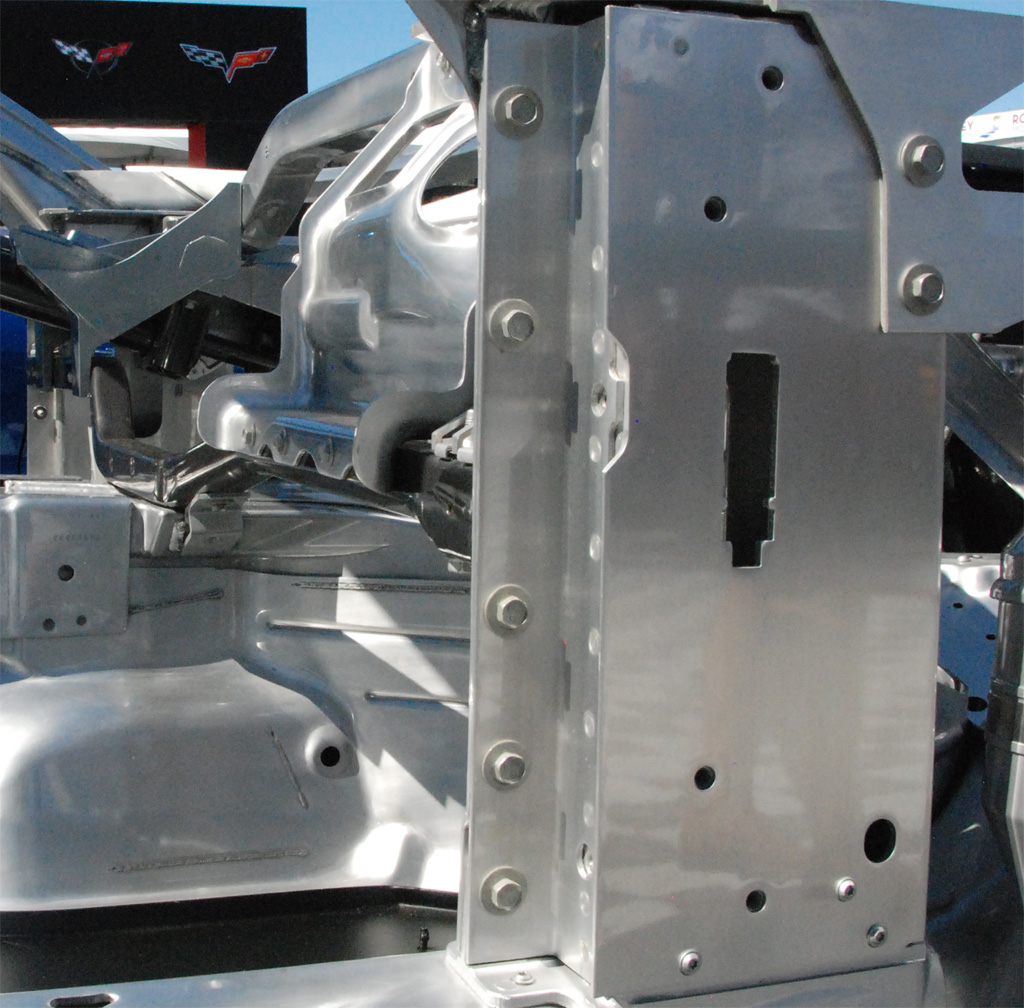
Above: Corvette chassis front door mount; below: rear door area..
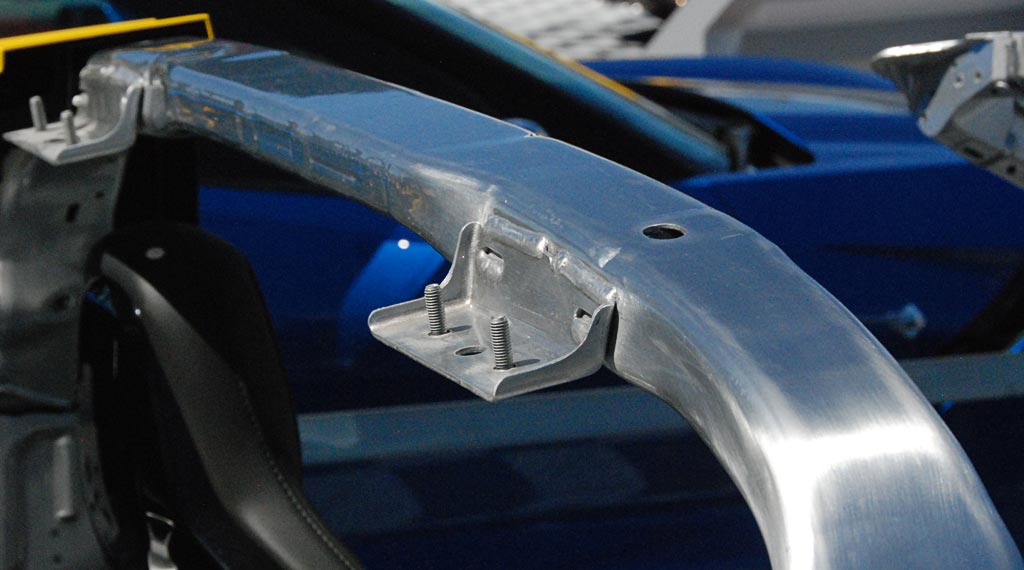
Chevrolet Corvette C7 roll hoop.
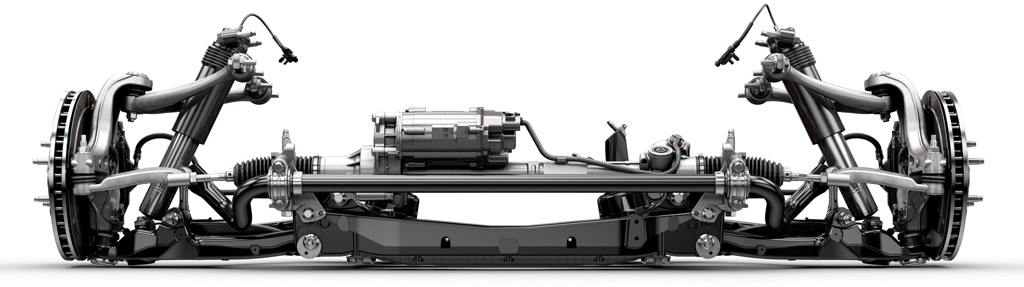
Changes to the front suspension include electrical power steering which offers variable ratios (12.0 to 16.4) and effort depending on driving situations and the selected driver mode. Better driver control and feedback are said to be amongst the benefits. Various structural improvements in the steering column and front cradle structure have also resulted in a more precise steering feel.
Above: Corvette C7 rear suspension. A transverse leaf spring is still used, which dates back to 1963 and the C2 generation when an independent rear suspension first made its debut on a Corvette. Since then composite materials have improved performance, and, GM engineers will tell you, it packages well.
Both the front and rear suspension cradles are hollow aluminum, enabling a 25% weight reduction and 20% improved stiffness over the solid steel C6 cradles.
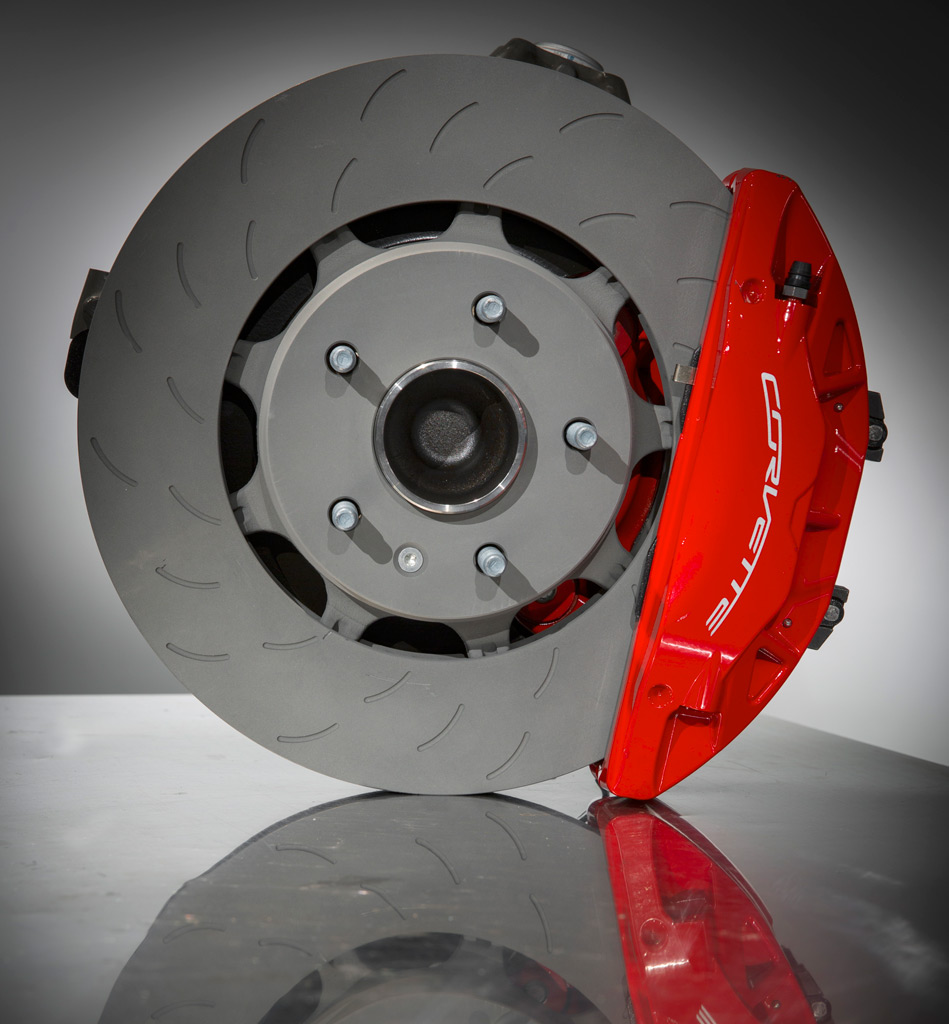
 Brembo brakes are standard on even the base model C7. The front features 12.6 inch rotors while the rear are larger at 13.3 inches. This adds up to 35% more swept area than could be found on the C6; stopping distance is claimed to have been improved by 9%. All C7 Corvettes have four piston calipers, front and rear.
Brembo brakes are standard on even the base model C7. The front features 12.6 inch rotors while the rear are larger at 13.3 inches. This adds up to 35% more swept area than could be found on the C6; stopping distance is claimed to have been improved by 9%. All C7 Corvettes have four piston calipers, front and rear.
The J55 Performance Brakes (included in the Z51 Performance Package option) option gets 13.6 inch front and 13.3 inch rear rotors, both slotted with dual cast rotors. This represents a 6% improvement in the swept area and a 5% stopping distance improvement over the previous generation Grand Sport models.
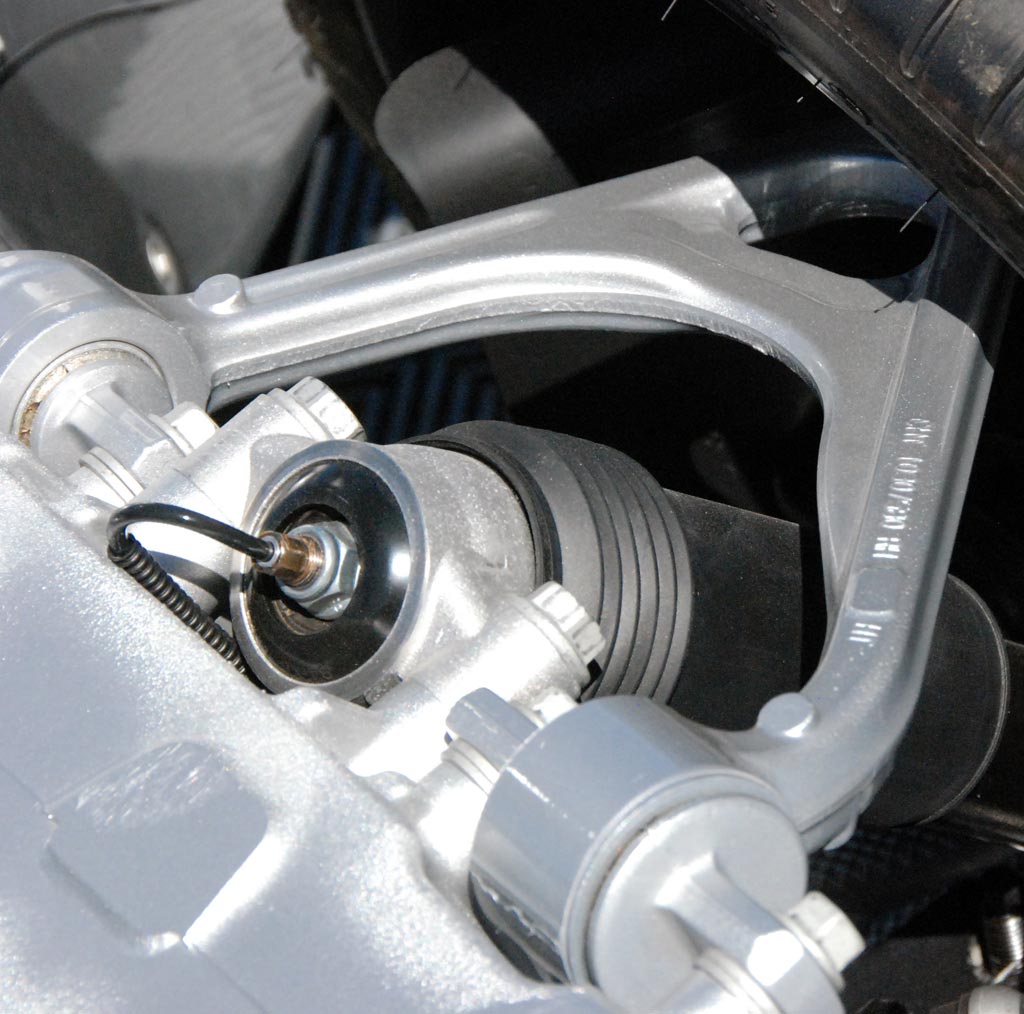
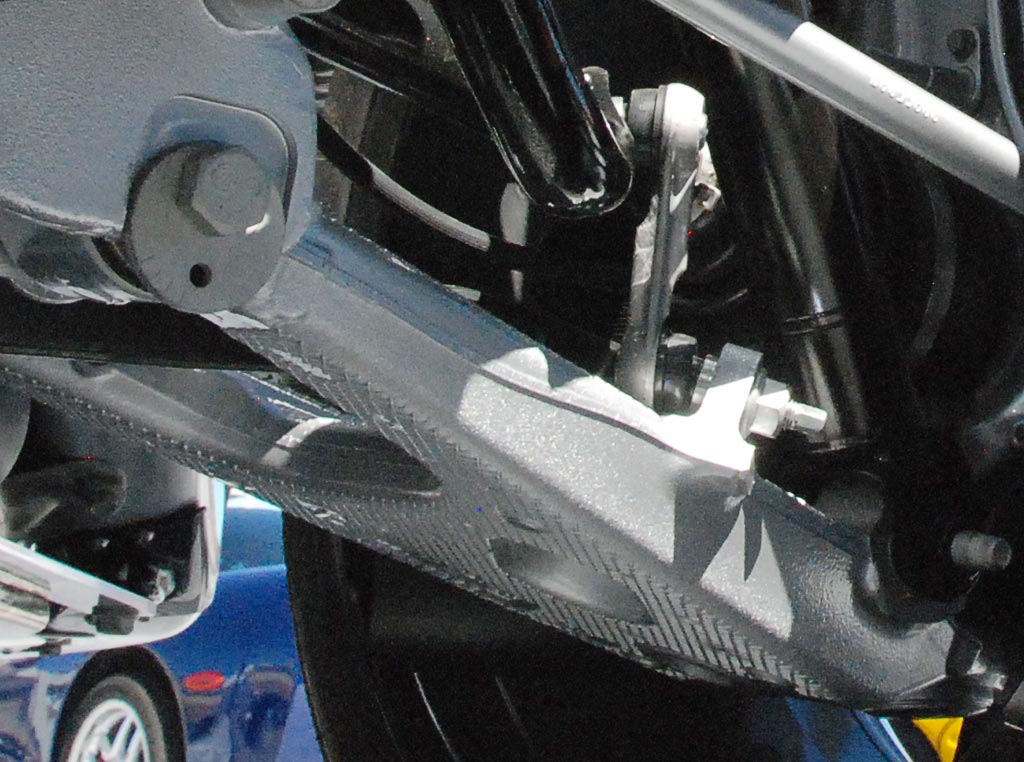
Above: C7 rear suspension A arms upper and lower (below) as installed. The SLA (Corvette speak for Short / Long A arms) geometry was basically unchanged from the C6; apparently the engineers could not find any improvements in that area.
The lower A arms are hollow cast aluminum saving about 4 kilograms (9 pounds) of weight for the entire car. They are also approximately 250% stiffer.
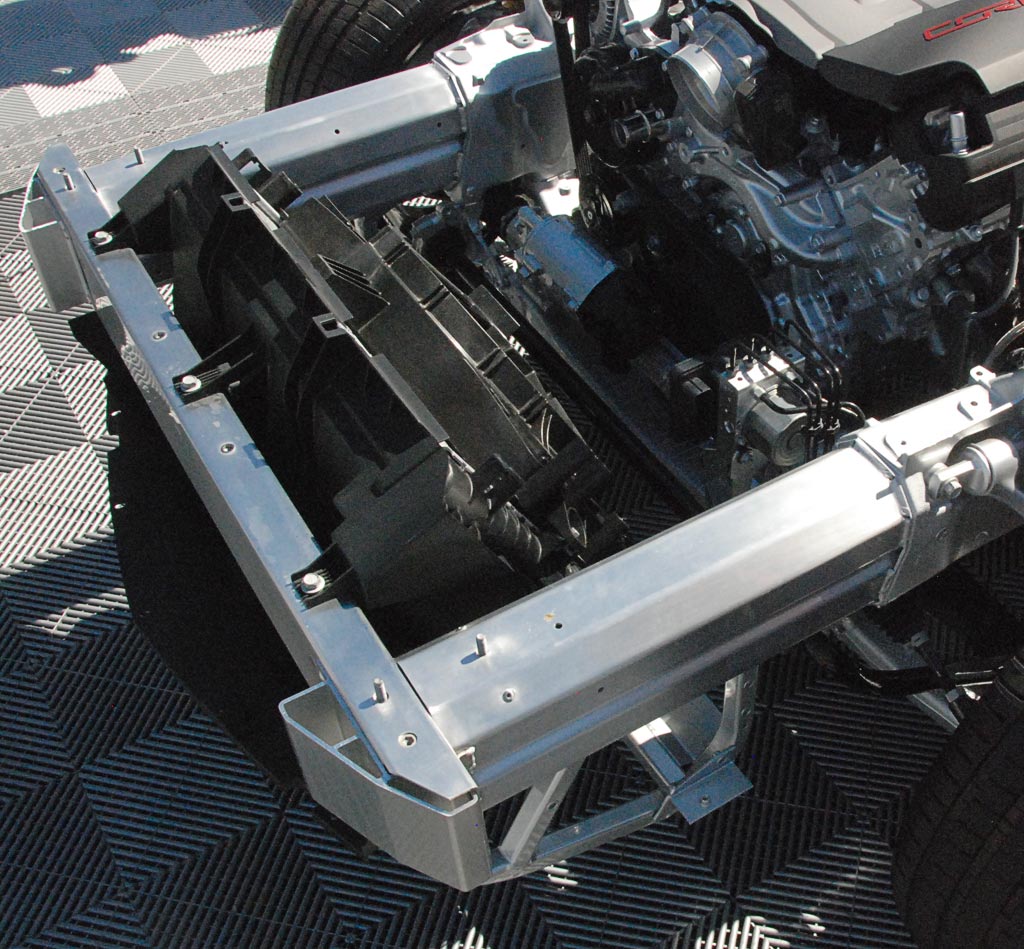
The floor construction, which included balsa wood as one of the sandwiched materials since the introduction of the C5 in 1997 was upgraded to a new carbon nano-composite floor pan that offered improved strength with less weight.
2014 Corvette Performance
More on the 2014 Corvette: |
||
| Styling | Interior | Engine |
| Chassis | Performance | Technology |
| Convertible | Instruments | Z51 |
| Evolution | Photographs | Specifications |